Article
Change Models
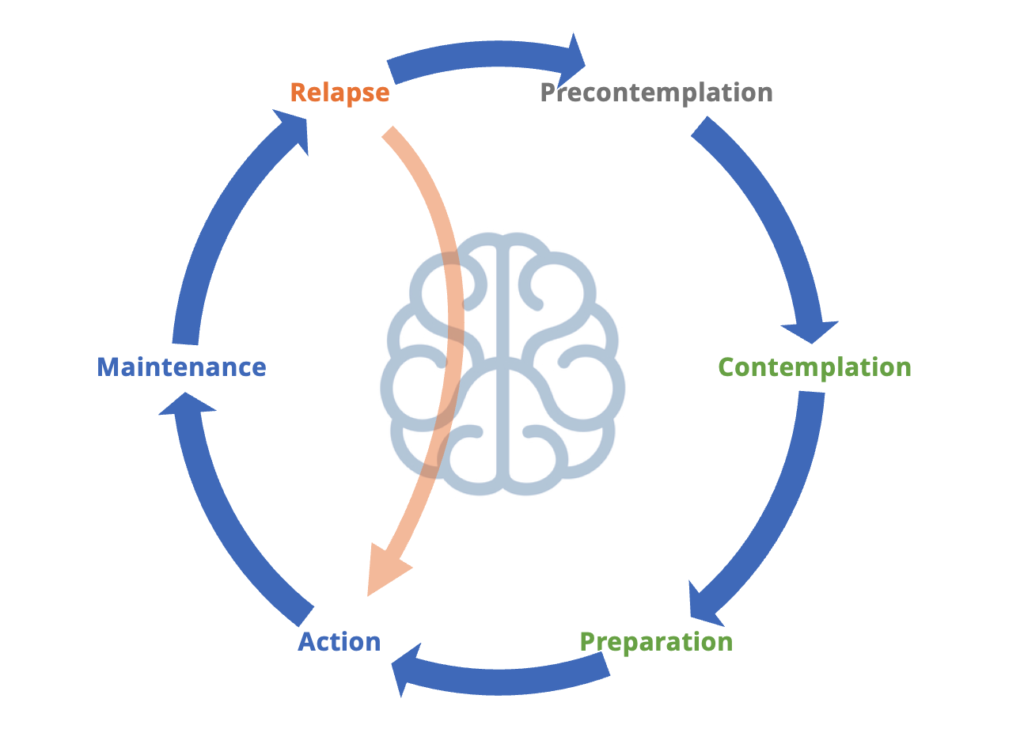
The 6 stages of change model is also known as the transtheoretical model and focuses on the steps of change. This has focused on changing individual’s behaviour to a new healthier behaviour.
These 6 steps are:
-
- Precontemplation – Pre-awareness. In this stage, people do not intend to take action in the foreseeable future (defined as within the next 6 months). People are often unaware that their behavior is problematic or produces negative consequences. People in this stage often underestimate the pros of changing behavior and place too much emphasis on the cons of changing behavior.
- Contemplation – Awareness. In this stage, people are intending to start the healthy behavior in the foreseeable future (defined as within the next 6 months). People recognize that their behavior may be problematic, and a more thoughtful and practical consideration of the pros and cons of changing the behavior takes place, with equal emphasis placed on both. Even with this recognition, people may still feel ambivalent toward changing their behavior.
- Preparation (Determination) – Decision and intention. In this stage, people are ready to take action within the next 30 days. People start to take small steps toward the behavior change, and they believe changing their behavior can lead to a healthier life.
- Action – Implementation. In this stage, people have recently changed their behavior (defined as within the last 6 months) and intend to keep moving forward with that behavior change. People may exhibit this by modifying their problem behavior or acquiring new healthy behaviors.
- Maintenance – In this stage, people have sustained their behavior change for a while (defined as more than 6 months) and intend to maintain the behavior change going forward. People in this stage work to prevent relapse to earlier stages.
- Relapse / Termination – Some version of the model put terminatoin i.e. the new behaviour is embedded and therefore the change process has finished. Arguably it stay in maintenance for a long period of time. Other version add “relapse” for when there is a relapse to old behaviours. this then leads bak to action phase.
This is guided by:
-
- Consciousness Raising – Increasing awareness about the healthy behavior.
- Dramatic Relief – Emotional arousal about the health behavior, whether positive or negative arousal.
- Self-Reevaluation – Self reappraisal to realize the healthy behavior is part of who they want to be.
- Environmental Reevaluation – Social reappraisal to realize how their unhealthy behavior affects others.
- Social Liberation – Environmental opportunities that exist to show society is supportive of the healthy behavior.
- Self-Liberation – Commitment to change behavior based on the belief that achievement of the healthy behavior is possible.
- Helping Relationships – Finding supportive relationships that encourage the desired change.
- Counter-Conditioning – Substituting healthy behaviors and thoughts for unhealthy behaviors and thoughts.
- Reinforcement Management – Rewarding the positive behavior and reducing the rewards that come from negative behavior.
- Stimulus Control – Re-engineering the environment to have reminders and cues that support and encourage the healthy behavior and remove those that encourage the unhealthy behavior.
Summary
The 6 stages of change give a guide through the temporal process of change, particularly for an indivudal. However, this can also be applied to institutions, initiatives, and corporations. It does not give clear guidance on the mechanism of change and when to use them. In contrast to other models this does not anaylse the drivers of behaviour such as attitudes, beliefs, and ability.
Simple Takeaways
-
- We can break change down into 6 stages
- This can guide thinking nad how to design interventions at each stage
© leading brains 2022
Reference
The transtheoretical model of health behavior change.
American Journal of Health Promotion, 12(1).
https://doi.org/10.4278/0890-1171-12.1.38
More Articles
To Change, Start Right Away
Sorry, stupid question right off the cuff. Change what?
Well, in this recent study they were looking at changing health behaviours.
Nudges Work In Changing People’s Behaviour
So what do you mean by “nudges”?
Richard Thaler is considered is one of the founding fathers of nudge theory in the behavioural sciences proposing nudges as the best method to modify people’s behaviour. Made popular by his book Nudge in 2008.
Followers Make Group Decisions a Lot Worse, or a Lot Better
First off, why is group decision-making important?
Well, a lot (just about all, if you think about it) of the biggest decisions in society and in business are made by groups: executive committees, governments, even the population in referendums.
The Right Rewards Boost Creativity in Business
So who doesn’t want to have creative ideas in their business.
The problem is getting employees to be creative while doing their day job as well. We also know that just asking or demanding creativity can diminish creativity and innovation!
Changing Your Personality — Even If You Don’t Want To!
Are you telling me that our personality can change even if we have no motivation to do so?
In a nutshell, yes. But it depends on which personality trait!
Exercise is Infectious
This is an older study (2017) I came across and found fascinating. As many of you regular readers will know I have reported many times on the benefits of exercise.
Why our Brains Miss Opportunities for Innovation
When we think of innovation we think of creating something new. A new study shows that, however, we, by default, try to add something whereby subtracting something could make something better.
Brain Region for Changing Behaviour Identified
The saying goes “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting different results.” This obviously refers to doing the same thing over and over and continually getting a bad result
From Couch to Ultra Marathon with Mental Imagery
On first glance I thought the above headline was fascinating. I am a sports person, look into the neuroscience of motivation, and have been in the “motivational” space for nigh on two decades.
Limits to Scalability – Voltage Drops
Voltage Drop is a useful term and analogy to the problems of scaling ideas or change in any environment. Voltage drop refers to how electrical current can decrease across distance it travels.










