Article
Change Models

When a combination of motivation and ability places a person above the activation threshold, then a prompt will cause that person to perform the target behavior. If a person is placed below the activation threshold, then a prompt will not lead to the target behaviour.
The B-MAT model is similar to the COM-B model included in the Behavioural Change Wheel which aims to explain behaviour and its antecedents and therefore aim to guide behavioural change attempts. It was put forward by BJ Fogg of the Persuasive Technology Lab of Stanford University. It is therefore also called the Fogg Behaviour Model (FBM)
B-MAT states that behaviour is a result of Motivation + Ability + Triggers. These are further broken down into key components.
Motivation:
-
- Sensation – these are our primitive motivations with little thinking or reflection involved.
- Anticipation – these are our reward (or fear) based motivation either through positivity, or financial, or alternative rewards.
- Belonging – is driven by our social desire to be part of a group and our sensitivity to social views and acceptance.
Ability:
-
- Time: The individual has the time to perform the target behaviour or the time taken is very low.
- Money: The individual has enough financial resources to pursue/start the behaviour. In some cases money can buy time.
- Physical effort: Target behaviours that require physical effort may not be simple enough to be performed.
- Brain cycles: Target behaviours that require high cognitive resources may not be simple hence undesirable for behaviour change.
- Social deviance: These include behaviours that make the user socially deviant. These kind of behaviours are not simple.
- Non-routine: Any behaviour that incurs disrupting a routine is considered not simple. Simple behaviours are usually part of routines and hence easy to follow.
Triggers
-
- Spark: The spark is a trigger that comes with added motivation. It’s perfect for those who have the ability but lack the motivation.
- Facilitator: While some people have the motivation, they still can’t achieve what they want to. For these people facilitation is needed either trhough guidance, or training, or support.
- Signal: Some people are ready to change. They have the motivation, they have the ability, all they need is the starting gun to fire and they’ll get going. Hence all they need is a spark.
Summary
B-MAT is a useful tool for analysing behaviour and particularly in indivdual case but also in larger scale initiatives. However, it fails to fully describe motivation (SCOAP is more accurate and comprehensive here). It also fails to include environmental contexts though some of these will be included in the Ability section.
It is still a useful and easy to understand guide for individual change.
Simple Takeaways
-
- Behaviour is driven by Motivation + Ability + Triggers
- B-MAT give you a framework to analyse behaviour and hence design interventions
© leading brains 2022
Reference
More Articles
The Nine Interventions
There have been multiple models of behaviour and behavioural change proposed over the years. These have taken different viewpoints of behaviour.
Two Types of Willpower
Will power can be different things – but not according to us everyday folk…
Mask-Wearing Makes You Better Behaved
This is a fascinating study that shows that wearing masks changes behaviour in subtle but important ways…
Behavioural Change Theories
There have been multiple models of behaviour and behavioural change proposed over the years. These have taken different viewpoints of behaviour.
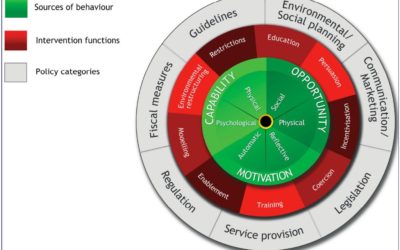
Behavioural Change Wheel
The Behaviour Change Wheel is the result of a systematic review of change models, frameworks, and theories, followed by the subsequent realisation that they were not aligned and describing different things.
Nudge
A nudge in everyday language is a gentle push. Something that is none aggressive but significant enough to be noticed and often triggers a behaviour…
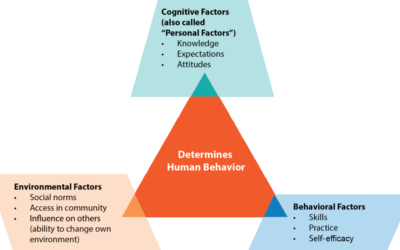
Social Cognitive Theory
Social Cognitive Theory by famed psychologist Bandura is grounded, as the name suggests, in social contexts saying that behaviour is driven by the triad of behaviour, personal, and environmental factors
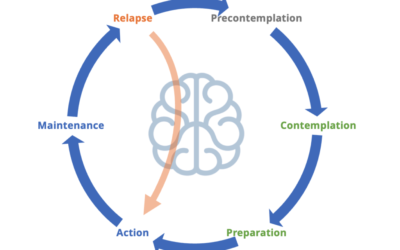
The 6 Stages of Behavioural Change
The 6 stages of change model is also known as the transtheoretical model and focuses on the steps of change. This has focused on changing individual’s behaviour to a new healthier behaviour.
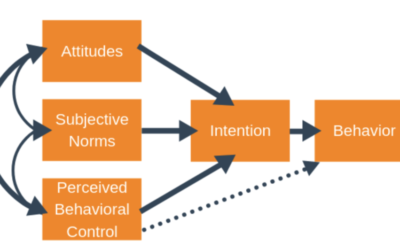
Theory of Planned Behaviour
he theory of planned behaviour is a psychological theory proposed by Icek Ajzen that links beliefs to behaviour. This builds on the theory of reasoned action
Don’t Try to Change Minds – Change Behaviour
Don’t try to change minds but simply change behaviour is the result a group of researchers have come to with regard to vaccinations.