Article
Change Models
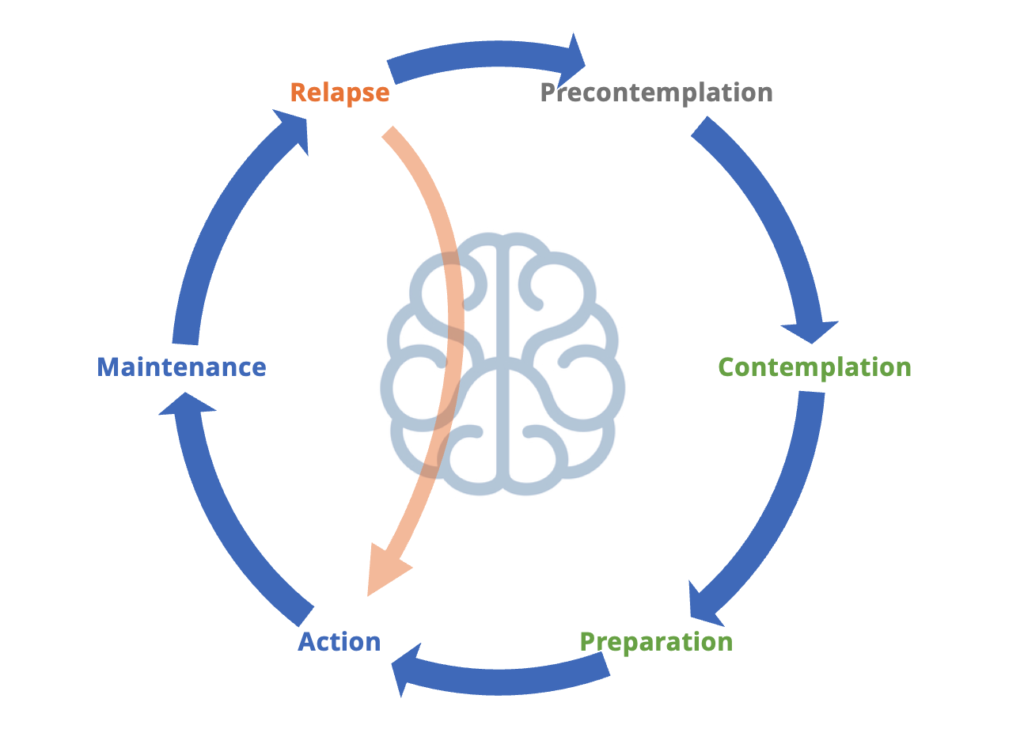
The 6 stages of change model is also known as the transtheoretical model and focuses on the steps of change. This has focused on changing individual’s behaviour to a new healthier behaviour.
These 6 steps are:
-
- Precontemplation – Pre-awareness. In this stage, people do not intend to take action in the foreseeable future (defined as within the next 6 months). People are often unaware that their behavior is problematic or produces negative consequences. People in this stage often underestimate the pros of changing behavior and place too much emphasis on the cons of changing behavior.
- Contemplation – Awareness. In this stage, people are intending to start the healthy behavior in the foreseeable future (defined as within the next 6 months). People recognize that their behavior may be problematic, and a more thoughtful and practical consideration of the pros and cons of changing the behavior takes place, with equal emphasis placed on both. Even with this recognition, people may still feel ambivalent toward changing their behavior.
- Preparation (Determination) – Decision and intention. In this stage, people are ready to take action within the next 30 days. People start to take small steps toward the behavior change, and they believe changing their behavior can lead to a healthier life.
- Action – Implementation. In this stage, people have recently changed their behavior (defined as within the last 6 months) and intend to keep moving forward with that behavior change. People may exhibit this by modifying their problem behavior or acquiring new healthy behaviors.
- Maintenance – In this stage, people have sustained their behavior change for a while (defined as more than 6 months) and intend to maintain the behavior change going forward. People in this stage work to prevent relapse to earlier stages.
- Relapse / Termination – Some version of the model put terminatoin i.e. the new behaviour is embedded and therefore the change process has finished. Arguably it stay in maintenance for a long period of time. Other version add “relapse” for when there is a relapse to old behaviours. this then leads bak to action phase.
This is guided by:
-
- Consciousness Raising – Increasing awareness about the healthy behavior.
- Dramatic Relief – Emotional arousal about the health behavior, whether positive or negative arousal.
- Self-Reevaluation – Self reappraisal to realize the healthy behavior is part of who they want to be.
- Environmental Reevaluation – Social reappraisal to realize how their unhealthy behavior affects others.
- Social Liberation – Environmental opportunities that exist to show society is supportive of the healthy behavior.
- Self-Liberation – Commitment to change behavior based on the belief that achievement of the healthy behavior is possible.
- Helping Relationships – Finding supportive relationships that encourage the desired change.
- Counter-Conditioning – Substituting healthy behaviors and thoughts for unhealthy behaviors and thoughts.
- Reinforcement Management – Rewarding the positive behavior and reducing the rewards that come from negative behavior.
- Stimulus Control – Re-engineering the environment to have reminders and cues that support and encourage the healthy behavior and remove those that encourage the unhealthy behavior.
Summary
The 6 stages of change give a guide through the temporal process of change, particularly for an indivudal. However, this can also be applied to institutions, initiatives, and corporations. It does not give clear guidance on the mechanism of change and when to use them. In contrast to other models this does not anaylse the drivers of behaviour such as attitudes, beliefs, and ability.
Simple Takeaways
-
- We can break change down into 6 stages
- This can guide thinking nad how to design interventions at each stage
© leading brains 2022
Reference
The transtheoretical model of health behavior change.
American Journal of Health Promotion, 12(1).
https://doi.org/10.4278/0890-1171-12.1.38
More Articles
The Equilibrium Effect
Things in life tend towards certain balances. This is particularly true in large systems and this is why change can happen in small contexts and be very effective or successful but in large systems different rules apply.
The supply side of scaling
There are a number of problems with the supply side – being able to supply the resources and competencies to drive change.
Unintended consequences and negative spillovers
We all know that any change – well, obviously, changes something. But this also means there will be various knock-on effects
Representativeness of the Situation
“You had to be there” is an expression that says you had to be in a particular situation, in that particular vibe, to fully understand a situation.
Representativeness of the Population
When we get a good idea, we may know it is a good thing. And because we know it is a good thing we may then falsely assume – without really thinking this through – that everybody thinks this is a good thing.
False Positives – The inference problem
A false positive has become better-known to the general public during the pandemic and with COVID-19 testing particularly with home based quick tests.






