There are a number of problems with the supply side – being able to supply the resources and competencies to drive change. The first and one of the most obvious ones is the financial side. How do finances change as ideas or concepts scale, or behavioural change programmes are implemented across organisations?
Often simple calculations are made that include upfront costs – but maintenance costs are often ignored. And change programme will require maintenance costs. Similarly, additional costs may not be considered. This therefore impacts and causes a voltage drop if the change programme is not financeable long-term.
Another problem with scaling is that of skills and competencies. Consider Michelin-starred restaurants. These are not restaurant chains, they are run by talented individual proprietors. They are not, and cannot be, chains of restaurants because the skills of the proprietor do not scale – they are very individualised. In contrast many successful social media companies are successful because they tap into human nature but are very scalable – posting pictures on Instagram is very scalable, anyone can do it (and does), as is reading or tweeting opinions on twitter.
This means we should be careful of trying to scale certain traits that are very individualised – or rather the larger we try to scale the simpler, easier, or clearer something should be. Companies often want to scale skills such as innovation or sales skills – but often these are individualised skills. Careful thought needs to be therefore given to what is scalable and how.
Simple Takeaways
-
- The larger the scale the simpler it must be
- Consider what is scalable
- Are the skills/behaviours unscalable or unchangeable?
© leading brains 2022
Reference
More Articles
The Nine Interventions
There have been multiple models of behaviour and behavioural change proposed over the years. These have taken different viewpoints of behaviour.
Two Types of Willpower
Will power can be different things – but not according to us everyday folk…
Mask-Wearing Makes You Better Behaved
This is a fascinating study that shows that wearing masks changes behaviour in subtle but important ways…
Behavioural Change Theories
There have been multiple models of behaviour and behavioural change proposed over the years. These have taken different viewpoints of behaviour.
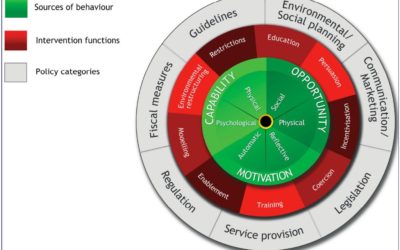
Behavioural Change Wheel
The Behaviour Change Wheel is the result of a systematic review of change models, frameworks, and theories, followed by the subsequent realisation that they were not aligned and describing different things.
Nudge
A nudge in everyday language is a gentle push. Something that is none aggressive but significant enough to be noticed and often triggers a behaviour…
B-MAT
The B-MAT model is similar to the COM-B model included in the Behavioural Change Wheel which aims to explain behaviour and its antecedents and therefore aim to guide behavioural change attempts
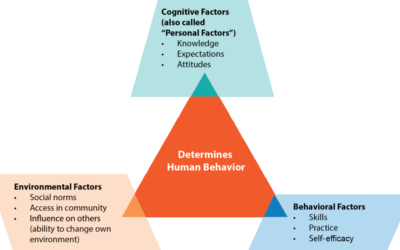
Social Cognitive Theory
Social Cognitive Theory by famed psychologist Bandura is grounded, as the name suggests, in social contexts saying that behaviour is driven by the triad of behaviour, personal, and environmental factors
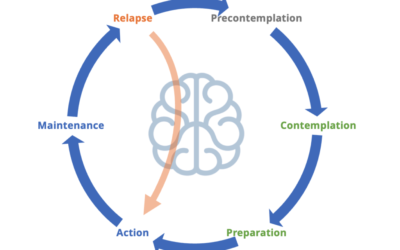
The 6 Stages of Behavioural Change
The 6 stages of change model is also known as the transtheoretical model and focuses on the steps of change. This has focused on changing individual’s behaviour to a new healthier behaviour.
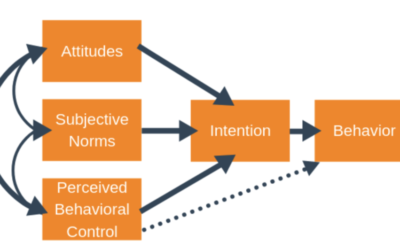
Theory of Planned Behaviour
he theory of planned behaviour is a psychological theory proposed by Icek Ajzen that links beliefs to behaviour. This builds on the theory of reasoned action